WEB TUTORIAL - Group Theory
[Re2Cl8]2- Worked Example
| D4h | E | 2C4 (z) | C2 | 2C'2 | 2C''2 | i | 2S4 | 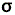 h h |
2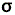 v v |
2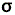 d d |
Rotations |
Functions |
Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1g | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | - | x2+y2, z2 | - |
| A2g | +1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | Rz | - | - |
| B1g | +1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | - | x2-y2 | - |
| B2g | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | - | xy | - |
| Eg | +2 | 0 | -2 | 0 | 0 | +2 | 0 | -2 | 0 | 0 | (Rx, Ry) | (xz, yz) | - |
| A1u | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | - | - | - |
| A2u | +1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | z | - | z3, z(x2+y2) |
| B1u | +1 | -1 | +1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | -1 | +1 | - | - | xyz |
| B2u | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | +1 | -1 | - | - | z(x2-y2) |
| Eu | +2 | 0 | -2 | 0 | 0 | -2 | 0 | +2 | 0 | 0 | (x, y) | - | (xz2, yz2) (xy2, x2y), (x3, y3) |
h = 16
Consider each symmetry element in turn, and answer how many unchanged bonds there are in each case after the symmetry element has been completed. This example is quite tricky but it will help to make a model, or to use the visualiser on the Otterbein Website.
The first number indicates the number of unchanged bonds for E, the second number
indicates the number of unchanged bonds for the C4 rotation and so forth.
-
E 2C4 C2 2C'2 2C"2 i 2S4
- 9 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 5 1
- 9 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 5 1
- 9 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 5 1